Why Do Cats Get Kidney Disease?
Cats can develop kidney disease due to various factors, such as age, genetic predisposition, and certain health conditions. This article will explore the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for feline kidney disease, providing helpful insights for cat owners concerned about their pet’s well-being.
Kidney disease is a common ailment among cats, affecting a significant number of feline companions. It can arise due to the natural aging process, as the kidneys gradually lose their ability to function properly. Additionally, certain breeds are more prone to this condition, suggesting a genetic component.
Furthermore, underlying health problems like high blood pressure or urinary tract infections can contribute to the development of kidney disease. Understanding the causes and risk factors of this condition is crucial for early detection and appropriate management, ultimately improving the quality of life for cats with kidney disease.
1. Understanding Kidney Disease In Cats
Kidney disease is a common health concern among cats, affecting a significant portion of the feline population. As a responsible cat owner, it’s essential to educate yourself about this condition and understand its causes, prevalence, and potential effects on your beloved pet’s overall well-being. In this section, we will delve into the details of what kidney disease is, how prevalent it is among cats, and what factors contribute to its development.
What Is Kidney Disease?
Kidney disease, also known as renal disease, occurs when a cat’s kidneys are no longer able to function optimally. The kidneys play a crucial role in removing waste products and excess fluids from the bloodstream, maintaining electrolyte balance, and producing important hormones. When these vital organs become impaired, it can lead to a range of health issues and even become life-threatening.
Prevalence Of Kidney Disease In Cats
Kidney disease is alarmingly prevalent in the feline population. Studies have shown that it affects around 30% of cats over the age of 10 and is one of the leading causes of death in older cats. This high prevalence underscores the importance of regular veterinary check-ups and early detection to manage the condition and provide the best possible care for your furry friend.
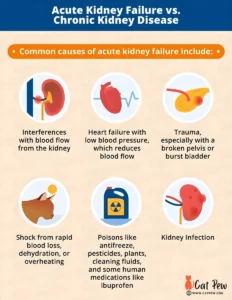
Causes Of Kidney Disease In Cats
While kidney disease can develop in cats of any age, it is more commonly observed in older felines. Numerous factors can contribute to the development of kidney disease in cats, including:
- Persistent dehydration: Cats with a low water intake, such as those on a dry food diet, are at a higher risk of kidney disease.
- Genetics: Some cat breeds, such as Persians, Abyssinians, and Siamese, have a higher predisposition to developing kidney disease.
- High blood pressure: Cats with hypertension are more prone to kidney disease as it can damage the blood vessels within the kidneys.
- Infections: Certain bacterial, viral, and fungal infections can directly affect the kidneys and contribute to their dysfunction.
- Toxic exposure: Exposure to certain toxins, such as antifreeze or certain medications, can damage the kidneys over time.
It’s important to note that kidney disease in cats is often a gradual process that may initially go unnoticed, as felines are masters at hiding their discomfort. Regular veterinary visits and screening tests are crucial to detect any signs of kidney disease early on, allowing for prompt intervention and a better prognosis.
2. Symptoms And Diagnosis
When it comes to kidney disease in cats, early detection is key to managing the condition effectively. By understanding the symptoms and diagnostic tests available, cat owners can ensure their furry friends receive appropriate care and treatment.
Common Symptoms Of Kidney Disease In Cats
If you suspect your cat may be suffering from kidney disease, it’s important to watch out for these common symptoms:
- Increased drinking and urination
- Loss of appetite or weight loss
- Bad breath
- Vomiting or diarrhea
- Weakness or lethargy
- Poor coat condition
These symptoms may vary in severity and can develop gradually over time. It’s crucial to consult with a veterinarian to accurately diagnose your cat’s condition.
Diagnostic Tests For Kidney Disease In Cats
To determine whether a cat has kidney disease, veterinarians rely on various diagnostic tests. These tests help provide a comprehensive understanding of the cat’s kidney function and overall health. The most common diagnostic tests for kidney disease in cats include:
- Blood tests: A panel of blood tests can evaluate kidney function, detect elevated levels of waste products, and assess other vital parameters such as blood cell counts. These tests help veterinarians assess the severity of kidney disease and develop an appropriate treatment plan.
- Urinalysis: Analyzing a cat’s urine can provide valuable insights into the health of their kidneys. Urine concentration, the presence of red or white blood cells, and the presence of protein or bacteria can indicate kidney disease.
- Imaging studies: Imaging techniques like X-rays or ultrasound may be used to visualize the structure and size of the kidneys. These tests can help identify any abnormalities or blockages in the urinary tract.
- Kidney biopsy: In certain cases, a veterinarian may recommend a kidney biopsy to obtain a small sample of tissue for microscopic analysis. This procedure provides crucial information about the underlying cause of kidney disease.
By utilizing these diagnostic tests, veterinarians can accurately diagnose kidney disease in cats and devise an individualized treatment plan.
3. Risk Factors

Understanding the risk factors for kidney disease in cats is crucial for cat owners and caregivers. By knowing and addressing these risk factors, we can take proactive steps to help prevent or manage this common feline health issue. Let’s explore the main risk factors in more detail:
Age And Breed Predisposition
Age and breed can play a role in a cat’s likelihood of developing kidney disease. As cats age, their kidneys can become less efficient at filtering waste products from the blood. This natural decline in kidney function is seen in many senior felines. Additionally, certain breeds are more predisposed to kidney disease than others. Persians, Siamese, and Abyssinians, for example, are known to have a higher risk of developing this condition.
Diet And Hydration
The diet and hydration status of cats can significantly impact their kidney health. High-quality, balanced diets that are specifically formulated for cats can help support overall kidney function. These diets are designed to provide essential nutrients while minimizing the workload on the kidneys. It’s important to note that excessive feeding of dry food, which has a low moisture content, may increase the risk of kidney disease. Proper hydration is crucial for cats, as it helps flush out toxins and maintain kidney function.
Other Health Conditions
Cats with certain underlying health conditions may be more susceptible to developing kidney disease. For instance, cats with high blood pressure, diabetes, or urinary tract infections may have an increased risk. These conditions can put additional strain on the kidneys and impact their ability to function optimally. Regular veterinary check-ups and timely management of these conditions can help reduce the risk of kidney disease in affected cats.
It’s important to keep in mind that while these risk factors can contribute to the development of kidney disease in cats, they do not guarantee that the condition will occur. Regular veterinary care, a balanced diet, and appropriate hydration are key components of kidney health maintenance for feline companions.
4. Effects On A Cat’s Body

Kidney disease can have various effects on a cat’s body, causing symptoms like increased drinking, frequent urination, weight loss, and decreased appetite. It can occur due to several factors, including genetics, aging, infections, and certain medical conditions such as high blood pressure or diabetes.
Regular check-ups and a balanced diet can help prevent and manage this condition.
When it comes to kidney disease in cats, the effects on their body cannot be ignored. The kidneys play a crucial role in maintaining a cat’s overall health and well-being. When these vital organs are compromised by disease, it can have widespread consequences throughout the cat’s body. From the function of the kidneys to the complications that arise, understanding the effects of kidney disease is essential for cat owners.
Function Of The Kidneys In Cats
The kidneys are responsible for filtering waste products and toxins from the cat’s blood, ensuring that only essential nutrients are retained. Additionally, these bean-shaped organs help maintain the balance of fluids and electrolytes in the body, regulate blood pressure, and produce hormones necessary for red blood cell production. When the kidneys become impaired due to disease, their ability to perform these vital functions diminishes. This can lead to a cascade of health issues and systemic imbalances that can drastically affect a cat’s overall well-being.
Complications Of Kidney Disease In Cats
Kidney disease in cats can give rise to a range of complications that impact various systems within their bodies. Some of the commonly observed complications include:
- Dehydration: As the kidneys cannot concentrate urine efficiently, cats with kidney disease often experience increased water intake and excessive urination. This can lead to significant fluid loss, resulting in dehydration.
- Electrolyte imbalances: With impaired kidney function, the delicate balance of electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, and calcium can be disrupted. These imbalances can affect nerve and muscle function, leading to weakness, muscle twitches, and seizures.
- Anemia: The kidneys produce a hormone called erythropoietin, which stimulates the production of red blood cells in the bone marrow. When kidney disease is present, erythropoietin production decreases, leading to a decrease in red blood cell production and resulting in anemia. Anemia can contribute to lethargy and weakness in cats.
- Hypertension: The kidneys help regulate blood pressure, and when they are not functioning optimally, hypertension (high blood pressure) can develop. Hypertension can damage various organs, including the eyes, heart, and brain.
- Urinary tract infections: Cats with kidney disease are more susceptible to urinary tract infections due to compromised immune function and impaired urine concentration. Understanding these complications is key to recognizing the signs of kidney disease in cats. Early detection and intervention are crucial in managing this progressive condition and improving a cat’s quality of life.
By staying informed and seeking veterinary care, cat owners can provide the necessary support to their feline companions.
5. Prevention
Preventing kidney disease in cats is crucial to ensure their overall health and well-being. By implementing a few key strategies, such as regular veterinary check-ups, proper hydration, and nutrition, as well as early detection and treatment, cat owners can significantly reduce the risk of their feline companions developing kidney disease.
Importance Of Regular Veterinary Check-ups
Regular veterinary check-ups play an integral role in preventing kidney disease in cats. These visits allow veterinarians to detect any potential issues early on before they progress into more serious conditions. During these check-ups, the veterinarian will conduct a thorough physical examination, evaluate blood work, and assess the cat’s overall health. By identifying any abnormalities or changes in kidney function, prompt intervention can be initiated to prevent further deterioration.
Proper Hydration And Nutrition
Providing cats with proper hydration and nutrition is crucial in maintaining their kidney health. Dehydration can put extra strain on the kidneys and impair their function. Cat owners need to ensure that their feline companions always have access to fresh water. Additionally, it is vital to feed them a balanced and nutritious diet specifically formulated for their age and health condition. A well-balanced diet that is high in moisture content and low in phosphorus can help promote healthy kidney function and reduce the risk of developing kidney disease.
Early Detection And Treatment
Early detection and treatment of kidney disease can significantly improve the prognosis for cats. Regular monitoring of urine output, blood pressure, and kidney function through routine veterinary check-ups can aid in the early identification of any potential kidney problems. If kidney disease is detected, prompt intervention can be initiated to slow down the progression of the disease and manage its symptoms. Treatment options may include dietary modifications, medication, and fluid therapy to support kidney function.
By focusing on prevention, cat owners can take proactive measures to safeguard their beloved pets from the risks of kidney disease. Regular check-ups, proper hydration, and nutrition, as well as early detection and treatment, are key to ensuring the long-term kidney health of cats.
6. Managing Kidney Disease
When it comes to managing kidney disease in cats, a comprehensive approach is crucial to ensure the well-being and quality of life of our feline friends. From medications and treatments to special dietary considerations and fluid therapy, implementing the right strategies can help slow the progression of the disease and alleviate its symptoms. Let’s delve into each aspect in more detail.
Medications And Treatments
Cats with kidney disease often require medications and treatments to manage the condition effectively. These may include:
- Phosphate binders: These medications help control high phosphate levels that often occur in cats with kidney disease.
- Blood pressure medications: Cats with kidney disease may develop hypertension, requiring medications to regulate blood pressure.
- Diuretics: These medications help increase urine production, promoting the elimination of toxins and reducing fluid buildup in the body.
- Anti-nausea medications: Cats with kidney disease may experience inappetence and vomiting, necessitating the use of anti-nausea drugs to stimulate appetite.
Special Dietary Considerations
Diet plays a crucial role in managing kidney disease in cats. A carefully tailored diet can help reduce the workload on the kidneys and provide essential nutrients. Some dietary considerations may include:
- Low-protein diet: Cats with kidney disease may benefit from a diet that is low in protein to minimize the buildup of waste products and to reduce the strain on the kidneys.
- Phosphorus restriction: Limiting phosphorous intake is essential to prevent further kidney damage. Specialized renal diets are often formulated to meet this requirement.
- Increased water intake: Encouraging cats with kidney disease to drink more water is vital to prevent dehydration and promote urinary tract health. Wet food or adding water to dry food can help increase water consumption.
Fluid Therapy
Fluid therapy is a critical component of managing kidney disease in cats. It helps support hydration, maintains electrolyte balance, and aids in flushing out toxins from the body. This therapy can be delivered via:
- Subcutaneous Fluid Administration: Subcutaneous fluids are administered under the skin to provide hydration and replace fluids lost due to increased urination.
- Intravenous Fluid Administration: In severe cases or during hospitalization, intravenous fluid administration may be necessary to deliver fluids and medications directly into the bloodstream.
By adhering to the recommended medications and treatments, implementing special dietary considerations, and providing appropriate fluid therapy, we can effectively manage kidney disease in cats, ensuring a better quality of life for our beloved furry companions.
7. Supportive Care

Cats with kidney disease require a calm and stress-free environment to promote their well-being and aid in their recovery. Creating a comfortable environment for your feline companion is crucial in minimizing stress levels and supporting their overall health.
To provide a peaceful atmosphere, consider the following:
- Designate a quiet and cozy space for your cat to rest. Provide a soft bed or blanket where they can feel secure and comfortable.
- Ensure the room temperature is kept at a comfortable level, avoiding extremes that may cause discomfort or additional stress.
- Minimize loud noises and sudden disruptions. Cats are sensitive to loud sounds, so keeping the environment as quiet as possible will help reduce stress.
- Install a scratching post and interactive toys to engage your cat and promote mental stimulation.
Proper litter box habits are essential for cats with kidney disease. Since their kidneys may not function optimally, it is crucial to monitor their urine output and maintain optimal hydration levels.
Consider the following tips to support your cat’s litter box habits:
- Provide a litter box that is easily accessible and comfortable for your cat to use. Ensure it is large enough for them to move around comfortably.
- Clean the litter box regularly to maintain cleanliness and hygiene. Cats are generally clean animals, and a dirty litter box can be a source of stress for them.
- Monitor your cat’s urine output and consistency. Changes in quantity or appearance may indicate underlying health issues, and it is essential to consult with a veterinarian.
- Ensure an ample supply of fresh water is available near the litter box. Adequate hydration is vital for cats with kidney disease.
Stress can exacerbate kidney disease in cats, impacting their overall well-being. As a pet owner, it is crucial to monitor and manage stress levels to support your cat’s health.
Here are some strategies to help reduce stress:
- Create a consistent routine for feeding, playtime, and relaxation. Cats thrive on predictability and having a structured routine can help alleviate stress.
- Provide hiding spots or elevated perches where your cat can retreat and feel safe.
- Avoid exposing your cat to stressful situations or introducing sudden changes, as this can cause anxiety.
- Consider using pheromone diffusers or calming aids to create a soothing environment.
By implementing supportive care measures such as creating a comfortable environment, maintaining good litter box habits, and monitoring and managing stress, you can help improve the quality of life for your beloved feline companion with kidney disease.
8. When To Consider Euthanasia

Kidney disease is a common ailment that can affect cats of all ages. It occurs when the kidneys become damaged and are no longer able to function properly. While this condition can often be managed through treatments and lifestyle changes, there may come a time when the quality of life for a cat with kidney disease becomes severely compromised. In such cases, veterinarians and pet owners may have to make the difficult decision of considering euthanasia.
Quality Of Life Assessment
A critical aspect of determining whether euthanasia is necessary for a cat with kidney disease involves assessing their quality of life. This assessment takes into account various factors that contribute to the overall well-being of the cat. Some key points to consider when evaluating a cat’s quality of life include:
- Appetite: Is the cat still eating and maintaining a healthy weight? A decrease in appetite and weight loss can indicate a decline in their overall health.
- Mobility: Can the cat move around comfortably? Kidney disease can cause weakness and difficulty in walking, affecting the cat’s ability to enjoy their usual activities.
- Pain: Is the cat experiencing pain that cannot be adequately managed? Chronic pain can greatly impact a cat’s quality of life and may indicate that euthanasia is a compassionate option.
- Hydration: Is the cat staying hydrated? Dehydration is a common issue in cats with kidney disease and can lead to further complications.
- Overall happiness: Does the cat still engage in activities they once enjoyed? Signs of depression or withdrawal may indicate a decline in their overall happiness.
Evaluating these factors and others related to a cat’s quality of life can provide valuable insight into their well-being and help guide the decision-making process.
Consulting With A Veterinarian
When faced with the difficult decision of euthanasia, seeking guidance from a veterinarian is crucial. A veterinarian has the expertise and experience to assess the physical and emotional condition of the cat, contributing to the decision-making process. They can provide valuable information on the cat’s prognosis, available treatment options, and other considerations.
Additionally, veterinarians can offer support to pet owners by discussing the potential benefits and drawbacks of euthanasia, ensuring that the decision is made with the best interest of the cat in mind. They can provide resources for grief counseling and assist in arranging a peaceful and compassionate euthanasia process, if necessary.
Making The Decision
Deciding to consider euthanasia for a cat with kidney disease is undoubtedly emotionally challenging. However, it is crucial to prioritize the best interests of the cat and their quality of life. Consulting with a veterinarian can help in weighing the available options and understanding the potential outcomes.
If the cat’s quality of life is significantly compromised, and their condition is unlikely to improve despite medical interventions, euthanasia may offer a humane alternative to alleviate their suffering.
Remember that this decision is always individual and deeply personal. By considering the cat’s quality of life, consulting with a veterinarian, and making an informed decision, pet owners can provide their beloved feline companions with the compassion and care they deserve.
9. Caring For A Cat With Kidney Disease
When it comes to caring for a cat with kidney disease, there are several important factors to keep in mind. Providing a balanced diet, administering medications, and scheduling regular vet visits are crucial in ensuring your furry friend’s well-being. By following these guidelines, you can help manage your cat’s kidney disease and promote their overall health.
Providing A Balanced Diet
A balanced diet plays a pivotal role in supporting your cat’s kidney function and preventing further damage. Specialized renal diets are available that are specifically formulated to support cats with kidney disease. These diets are low in protein and phosphorus, which helps ease the workload on the kidneys.
Furthermore, it’s important to keep your cat hydrated. Encourage them to drink plenty of water by providing fresh water sources throughout the house. Additionally, you can incorporate wet food into their diet, as it contains a higher water content compared to dry kibble. However, always consult with your vet before making any changes to your cat’s diet.
Administering Medications
Administering medications as prescribed by your vet is crucial for managing your cat’s kidney disease. Medications such as ACE inhibitors, phosphorus binders, and potassium supplements may be prescribed to help support kidney function and maintain the balance of important minerals in the body.
Ensure you follow the vet’s instructions meticulously regarding medication dosage and frequency. If your cat refuses to take medication, consult your vet for alternative administration methods, such as using a pill pocket or mixing medication into their food.
Regular Vet Visits And Monitoring
Scheduling regular vet visits is essential in monitoring your cat’s kidney disease and adjusting their treatment plan accordingly. During these visits, your vet will conduct blood tests, urine analysis, and measure blood pressure to evaluate your cat’s kidney function and overall health.
Additionally, your vet may recommend performing regular ultrasounds or X-rays to monitor the progression of the kidney disease. These diagnostic tests provide valuable insights into the current state of your cat’s kidneys, allowing for timely interventions if necessary.
In conclusion, caring for a cat with kidney disease requires a comprehensive approach that focuses on providing a balanced diet, administering medications as prescribed, and scheduling regular vet visits. By adhering to these guidelines, you can help improve your cat’s quality of life and effectively manage their kidney disease.
10. Research And Future Developments

When it comes to understanding kidney disease in cats, ongoing research and future developments are crucial in improving treatment options, prevention methods, and early detection. Veterinary scientists and researchers are continuously studying this condition to enhance the lives of our feline companions.
Advancements In Treatment Options
In recent years, significant strides have been made in the treatment of kidney disease in cats. Veterinarians now have a range of options to manage this condition and slow down its progression. One exciting advancement is the development of pharmaceutical treatments that specifically target the underlying causes of kidney disease in cats. These targeted therapies offer hope for improved kidney function and a better quality of life for our furry friends.
In addition to pharmaceutical treatments, veterinarians also have access to advanced renal diets that are specially formulated to support kidney health. These diets are low in phosphorus and contain high-quality protein sources to help reduce the workload on the kidneys. They also often include Omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and other beneficial nutrients to provide optimal support.
Studies On Prevention And Early Detection
Preventing kidney disease in cats is an important goal for researchers and veterinarians alike. Through comprehensive studies, scientists are gaining valuable insights into the risk factors associated with kidney disease in cats, such as age, breed, genetics, and environmental factors.
Ongoing research is also focused on developing improved methods for the early detection of kidney disease in cats, as early intervention is crucial for the successful management of the condition. Veterinarians are exploring innovative techniques and blood tests that can detect early signs of kidney dysfunction before significant damage occurs. These advancements in early detection will enable veterinarians to initiate appropriate treatment sooner, slowing down disease progression and extending the lifespan of affected cats.
Promising Therapies And Technologies
In the field of veterinary medicine, promising therapies and technologies are constantly being studied and developed for the treatment of kidney disease in cats. Stem cell therapy is one such area of interest, as it holds the potential to regenerate damaged kidney tissue and improve kidney function.
Researchers are also exploring the role of genetics in kidney disease, aiming to identify genes that may predispose certain cat breeds to this condition. By understanding the genetic factors involved, it may be possible to develop targeted prevention strategies and treatments tailored for specific breeds.
Additionally, there is ongoing research into biomarkers for kidney disease in cats. Biomarkers are measurable substances in the body that can indicate the presence or progression of a disease. Developing reliable biomarkers for kidney disease will not only aid in early detection but also help in monitoring response to treatment and evaluating treatment efficacy.
| Treatment/Technology | Description |
|---|---|
| Stem Cell Therapy | Regenerates damaged kidney tissue, improving function |
| Genetic Studies | Identifying genetic factors associated with kidney disease in specific cat breeds |
| Biomarkers | Measurable substances that indicate the presence and progression of kidney disease |
These research efforts hold great promise for future advancements in the diagnosis, treatment, and prevention of kidney disease in cats. With continued dedication to scientific study, veterinarians and researchers are making significant progress toward improving the lives of cats affected by this condition.
Conclusion Of Why Do Cats Get Kidney Disease
Cats are at risk of developing kidney disease due to various factors such as age, genetics, and certain health conditions. Understanding the causes is crucial to prevent and manage this condition effectively. By providing a balanced diet, maintaining hydration, and regular veterinary check-ups, cat owners can promote kidney health and prolong their feline companion’s life. Stay proactive about your cat’s wellbeing to ensure a healthy and happy life together.
Frequently Asked Questions Of Why Do Cats Get Kidney Disease?
What Is Kidney Disease In Cats?
Kidney disease, also known as renal disease, refers to a condition where a cat’s kidneys are unable to function optimally, leading to a gradual loss of kidney function over time.
What Are The Symptoms Of Kidney Disease In Cats?
Common symptoms include increased thirst and urination, weight loss, decreased appetite, lethargy, vomiting, and changes in coat quality. Regular veterinary check-ups are crucial to detect early signs.
How Do You Prevent Kidney Disease In Cats?
To prevent kidney disease in cats: 1. Provide fresh water to keep them hydrated. 2. Feed a balanced diet and avoid excessive amounts of protein. 3. Regularly check their blood pressure and monitor their urine. 4. Maintain a healthy weight through exercise and portion control. 5. Visit the vet for regular check-ups and consider annual blood and urine tests.
What Causes Cat’s Kidney Failure?
The main cause of kidney failure in cats is usually chronic kidney disease (CKD), which is a progressive deterioration of the kidneys. Other common causes include infections, toxins, urinary tract obstructions, and certain medications. Regular check-ups and a balanced diet can help prevent kidney problems in cats.
Are Certain Cat Breeds More Prone To Kidney Disease?
Some cat breeds may have a genetic predisposition to kidney issues. Persian and Siamese cats, for example, are known to be more susceptible. However, kidney disease can affect cats of any breed.
Can Infections Contribute To Kidney Disease In Cats?
Yes, bacterial or viral infections, especially those affecting the urinary tract, can contribute to kidney disease. It’s important to address and treat infections promptly to reduce the risk of kidney complications.
Does Dry Cat Food Cause Kidney Disease?
Dry cat food does not directly cause kidney disease. However, a diet solely consisting of dry food may increase the risk. Cats need to have a balanced diet, including wet food, to maintain kidney health.
At What Age Do Cats Get Kidney Disease?
Cats can develop kidney disease at any age, but it is more common in older felines.

Winston
I'm Winston, the author of this feline-focused (Catpew.com) blog . My love for cats goes back to my childhood, when I spent countless hours playing with my family's tabby, Mittens. This furry friend instilled in me a deep appreciation for the unique personalities, playful nature, and unconditional love that cats offer.